

Car Park Co Sensor Calibration
First and foremost, carbon monoxide (CO) sensor calibration is a critical life-safety requirement for anyone managing or owning a building—whether commercial, residential, or industrial.
Any property with an enclosed or semi-enclosed car park that does not have adequate natural ventilation is required to ventilate the space using mechanical ventilation systems. These systems typically rely on carbon monoxide sensors to activate and regulate airflow based on actual CO levels.
Under the Occupational Safety and Health Act (Section 21), building owners and managers have a legal obligation to ensure that:
- CO-controlled ventilation systems are regularly tested and serviced
- Accurate records of testing and calibration are maintained
- Carbon monoxide levels do not exceed prescribed exposure standards
Because CO sensors can drift over time due to environmental conditions, exhaust particulates, and general ageing, six-monthly testing and calibration is required to ensure they are reading accurately and responding correctly.
Carbon monoxide sensor testing and calibration is classified as an essential service, helping to:
- Protect occupants and workers from harmful CO exposure
- Ensure ventilation systems operate as designed
- Maintain compliance with safety legislation and insurance requirements
- Reduce liability for property owners and managers
Regular calibration isn’t just best practice—it’s a legal, operational, and moral responsibility to safeguard people and property.
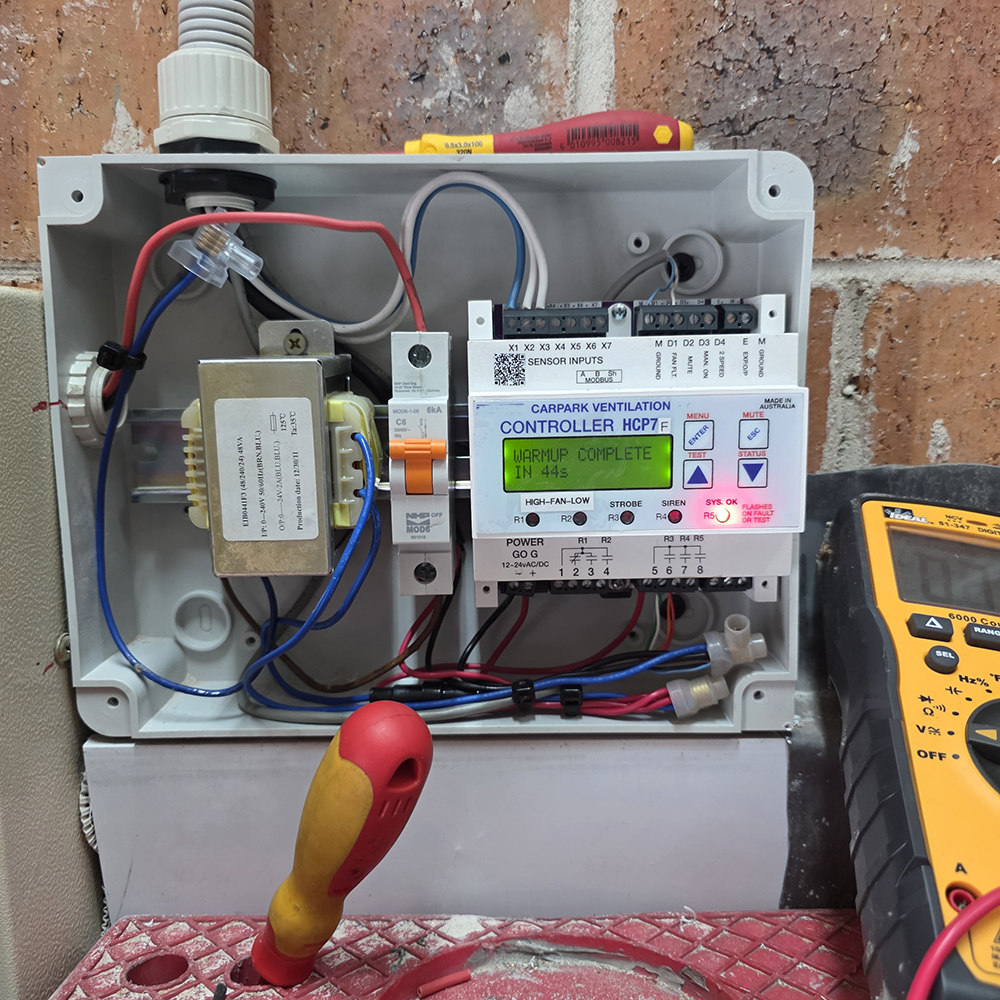
How Does the Carbon Monoxide Sensor System Work?
A carbon monoxide (CO) gas sensor detects the presence of CO using an electrochemical sensing element that naturally degrades over time, which is why regular calibration is essential. The sensor sends a control signal (typically 4–20 mA or 0–10 V DC) to the car park ventilation controller.
When CO levels rise above the programmed set points, the controller activates the exhaust fans. If variable speed drives (VSDs) are installed, fan speed is progressively increased in proportion to the detected CO concentration.
Typical operating parameters are:
- ~8 ppm: Fans start and run for a minimum of 4 minutes
- 24 ppm: Fans operate at 100% capacity
- Fans may only stop once CO levels return to 0 ppm for at least 4 minutes, and the system has operated for a minimum total runtime of 7 minutes
- A high CO alarm is annunciated at 35 ppm after 1 minute
This staged control strategy ensures effective dilution of exhaust gases while maintaining occupant safety and regulatory compliance.
What is a Varible Speed Drive (VSD)?
Variable Speed Drives (VSDs) are used primarily to improve energy efficiency and reduce mechanical stress on car park ventilation systems. By providing a soft start for exhaust fans, a VSD significantly lowers inrush current compared to Direct On Line (D.O.L) starting.
A D.O.L start can draw up to three times the fan’s nominal running current at start-up. In contrast, a VSD limits current draw, reducing electrical demand and minimising wear and tear on motors, bearings, belts, and associated mechanical components—extending overall equipment life.
Because fan speed is modulated in response to real-time carbon monoxide (CO) levels, the system often does not need to reach 100% fan speed to effectively ventilate the car park. Once CO levels are reduced and the sensor returns to zero, the fans can ramp down or stop, delivering further energy savings without compromising safety.
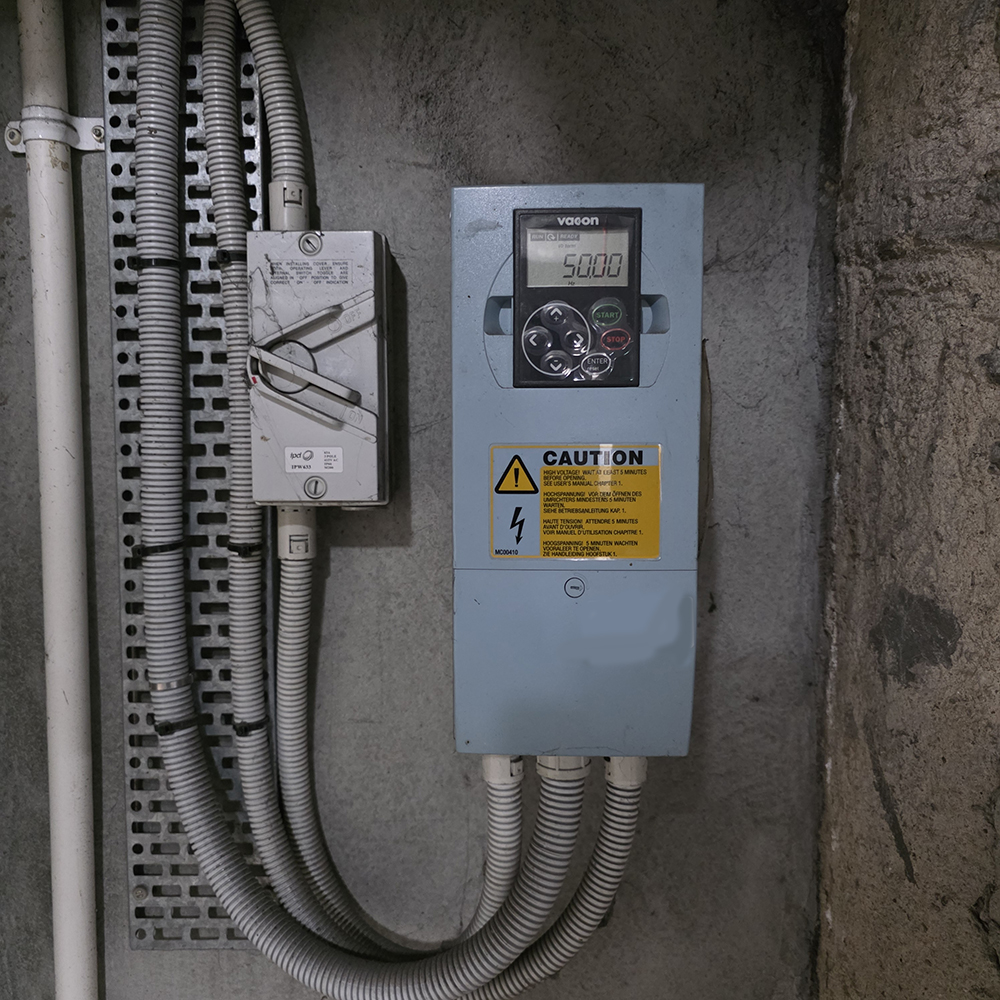

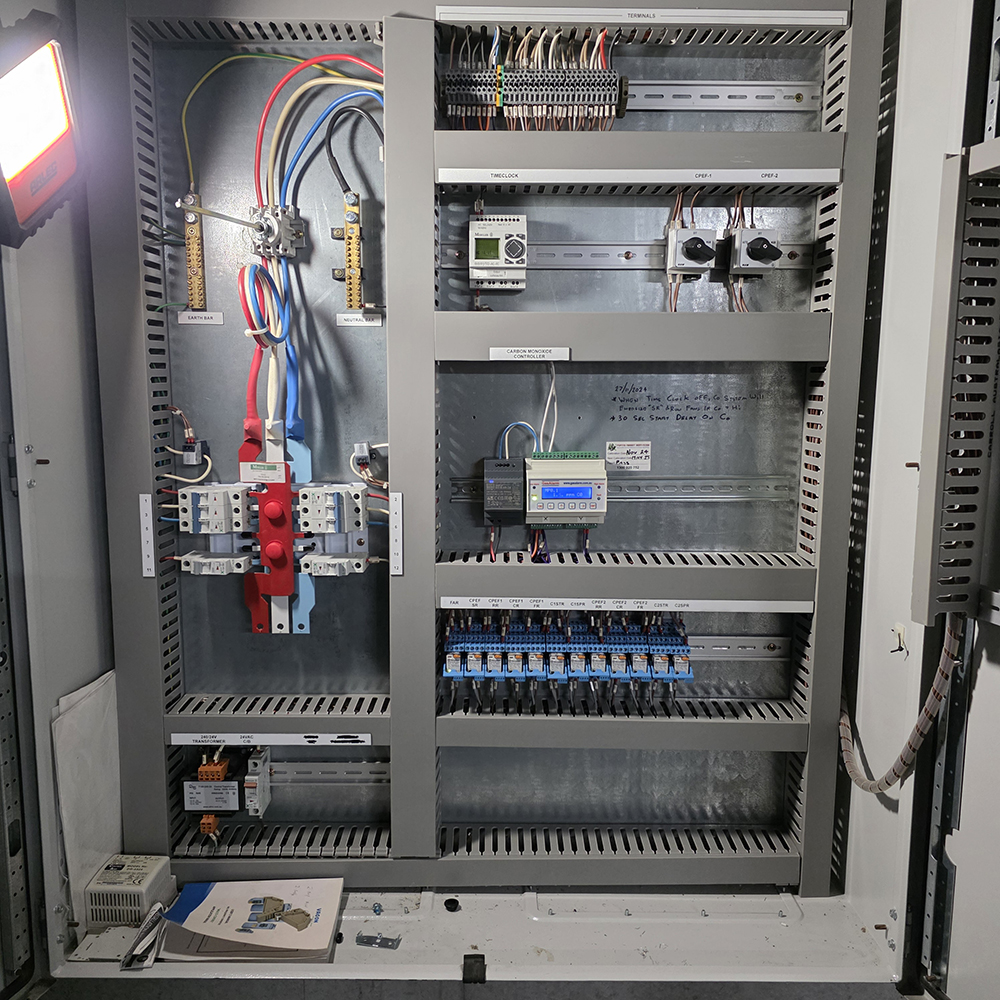
Is it part of Essential Services?
Compliance & Essential Services
- Governing Standard: AS 1668.2 – Ventilation of enclosed spaces (Section 4 – Car Parks)
- Essential Services: Yes
CO-controlled car park ventilation systems form part of a building’s essential life safety services and must be maintained, tested, and recorded accordingly.
Our Service Offering
As a company servicing fire systems, mechanical HVAC systems, and electrical services, we are uniquely positioned to deliver carbon monoxide sensor calibration efficiently and compliantly.
This service is available:
- As part of an integrated essential services maintenance package, or
- As a stand-alone calibration service
Ensuring accuracy, compliance, and energy-efficient operation of your car park ventilation system.
What is Involved in Performing a Six Monthly Test on the car park ventilation System?
Carbon Monoxide (CO) Ventilation System – Testing, Calibration & Inspection
In accordance with AS 1668.2 – The use of mechanical ventilation in buildings and WHS requirements for exposure to airborne contaminants, the following services will be carried out:
Record Keeping: Supply a log suitable for client records, WHS compliance, and regulatory audits.
Operational Testing of CO Sensors: Verify correct operation of all Carbon Monoxide sensors using certified calibration gas (“Cal Gas”).
CO Sensor Calibration: Perform calibration with 100 ppm certified Cal Gas to ensure sensors provide accurate readings in compliance with safety standards.
Inspection of Mechanical Ventilation Equipment: Assess the physical condition of all ventilation fans for integrity, wear, and obstructions.
Electrical Performance Checks: Measure and record current draw of fan motors and Variable Speed Drives (VSD) to confirm correct operation and energy efficiency.
Time Clock Verification: Confirm the presence and correct operation of any installed time clocks controlling fan operation.
Compliance Labelling: Affix calibration stickers to each CO sensor, clearly indicating the test/calibration date.
Reporting: Provide a comprehensive service report detailing inspection findings, test results, and recommendations for any corrective actions.
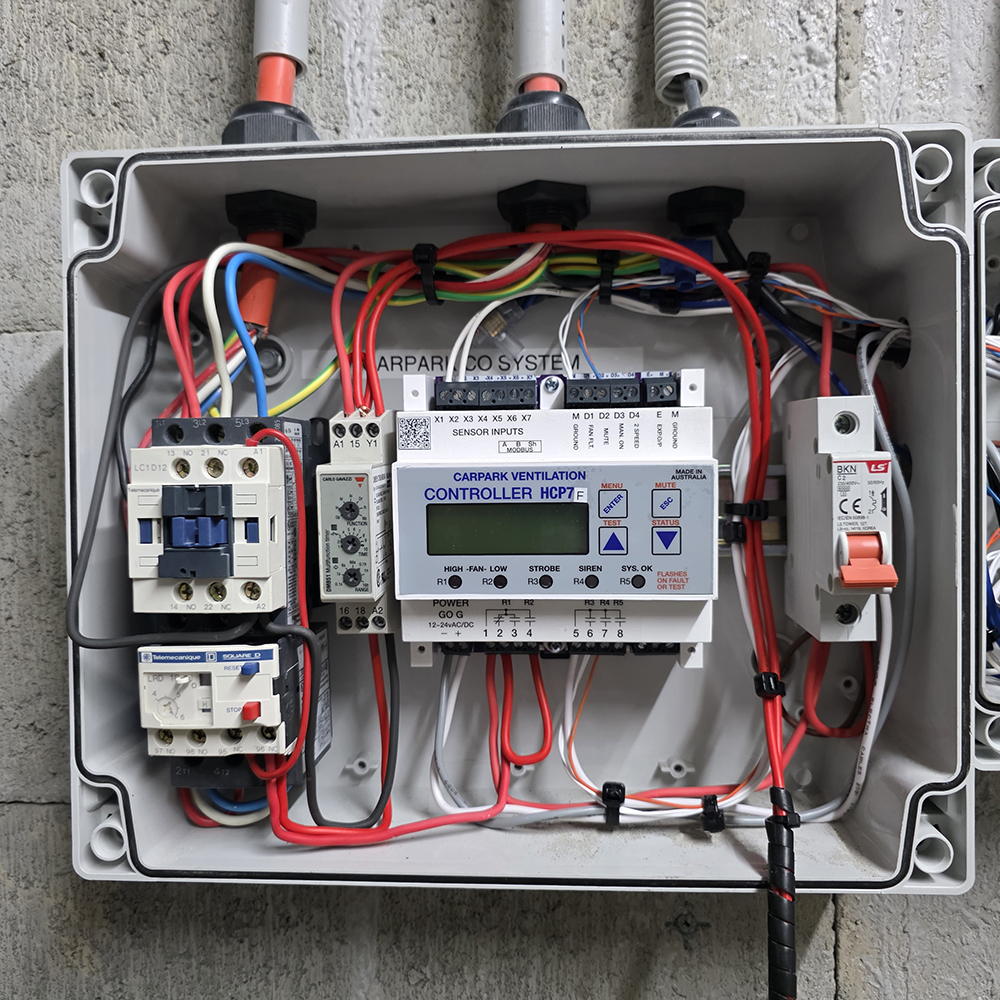
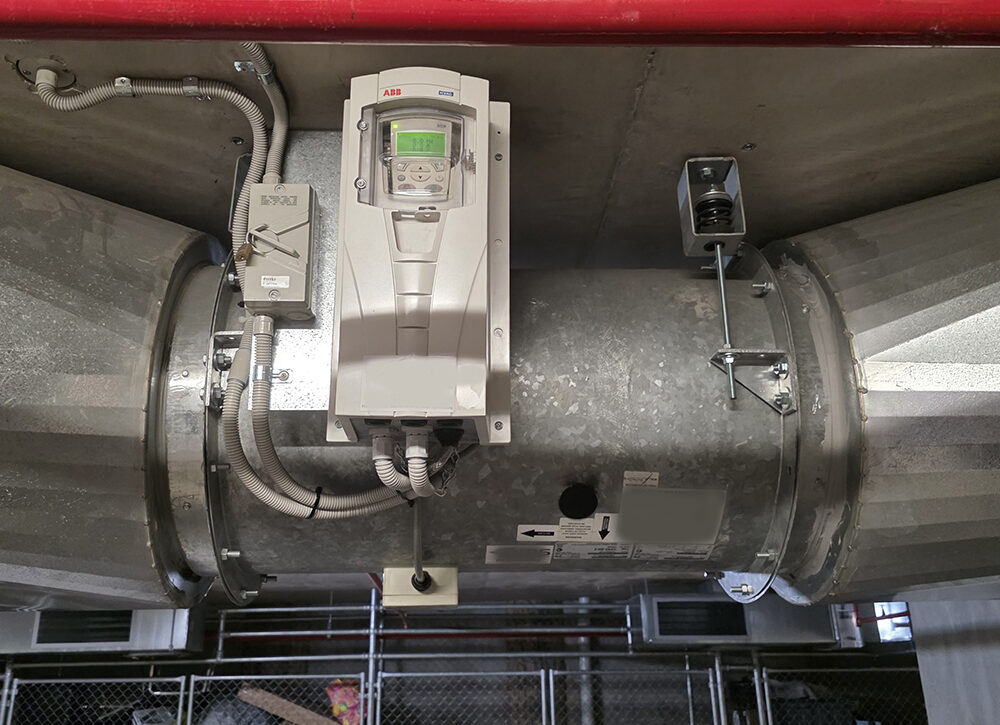
Carbon Monoxide (CO) Ventilation System Compliance Procedure
The CO monitoring and ventilation system shall be serviced every six months to ensure ongoing operational safety and regulatory compliance. Sensors must be positioned so that no point in the car park is more than 25 metres from a sensor to guarantee adequate coverage. In the event of a sensor fault, the system shall operate at 100% capacity to maintain safe air quality levels. The system must also ensure that the air in the car park is fully exchanged at least once every 24 hours, using either a purge or flush cycle, to prevent the accumulation of hazardous gases. All service and operational records must be documented and retained for compliance verification.